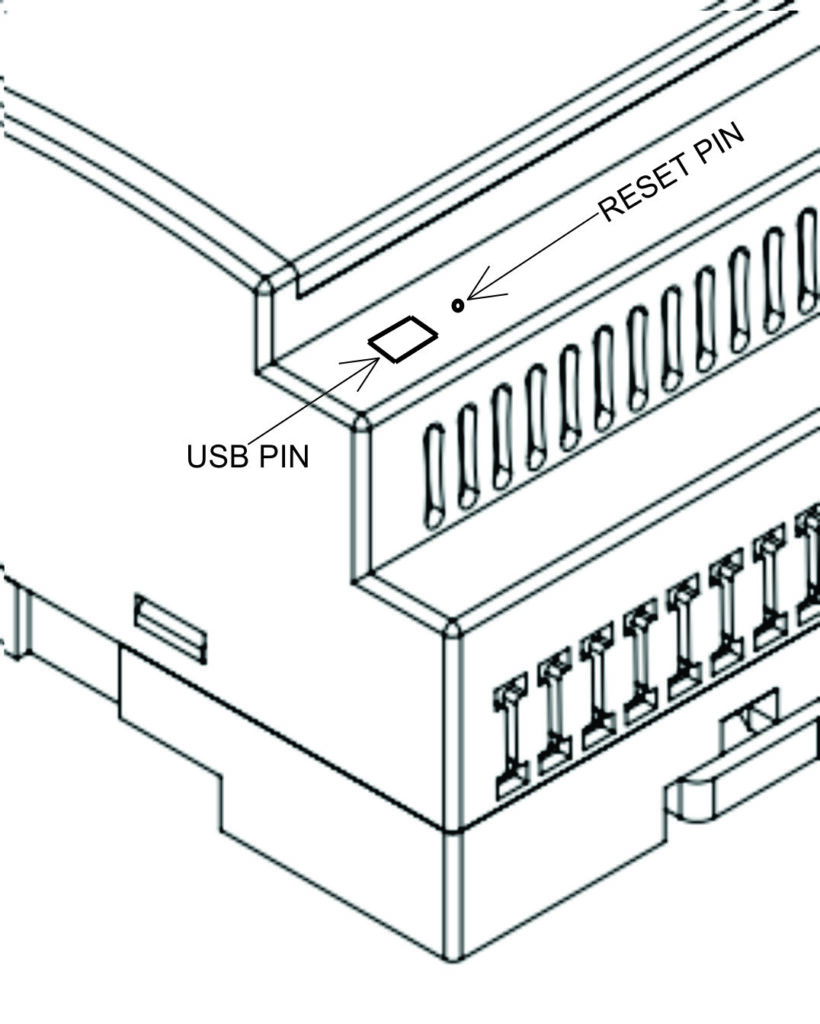
Programming #
The NORVI GSM-AE07-R-G has a mini USB Port for serial connection with the SoC for programming. Any ESP32-supported programming IDE can be used to program the controller. Follow this Guide to programming NORVI ESP32-based controllers with the Arduino IDE.
SoC: ESP32-WROOM32
Programming Port: USB UART
Digital Inputs #
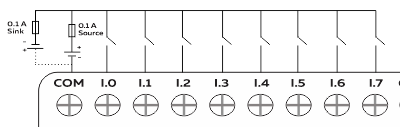
Wiring Digital Inputs #
The digital inputs of the NORVI GSM-AE07-R-G can be configured as both Sink and Source connections. The inverse of the Digital Input polarity should be supplied to the common terminal.
Programming Digital Inputs #
Reading the relevant GPIO of the ESP32 gives the value of the Digital Input. When the inputs are in the OFF state, the GPIO goes HIGH, and when the input is in the ON stage, the GPIO goes LOW. Refer to the GPIO allocation table in the datasheet for the digital input GPIO.
#define INPUT1 35
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Device Starting");
pinMode(INPUT1, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT1));
Serial.println("");
delay(500);
}Relay Output #
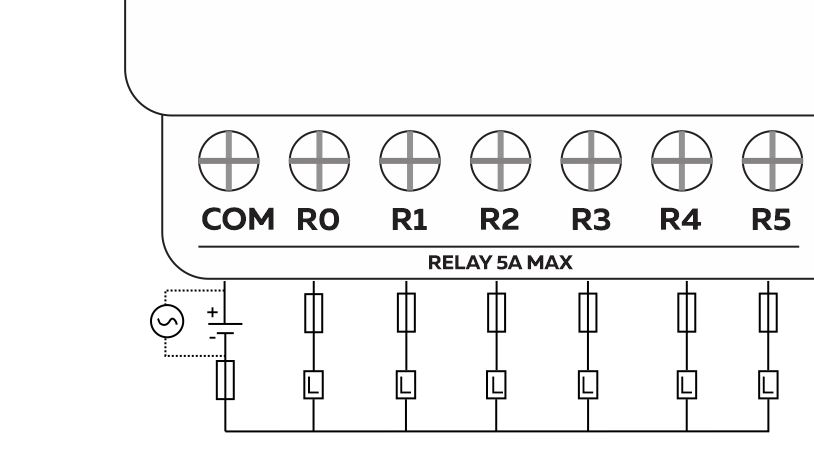
Wiring Relay Outputs #
Programming Relay Outputs #
Reading the relevant GPIO of the ESP32 gives the value of the relay or transistor output. Refer to the GPIO allocation table in the Datasheet for the relay/transistor output GPIO.
#define OUTPUT1 12
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Device Starting");
pinMode(OUTPUT1 , OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(OUTPUT1, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(OUTPUT1, LOW);
delay(500);
Serial.println("");
delay(500);
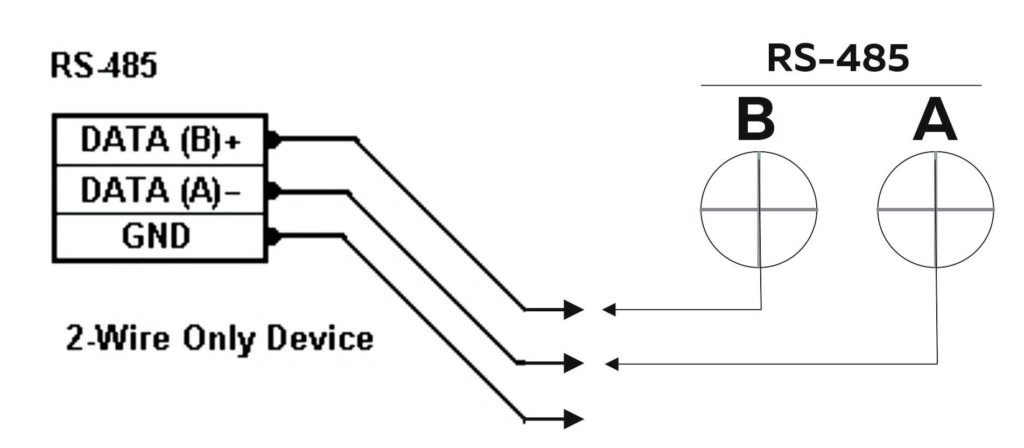
}RS-485 Communication #
| Driver | MAX485 |
| UART RX | GPIO25 |
| UART TX | GPIO19 |
| Flow Control | GPIO22 |
Programming RS-485 #
NORVI-GSM-AE07 series RS-485 connection uses a half-duplex mode of MAX485 transmitter with UART communication.
#define RXD 25
#define TXD 19
#define FC 22
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(FC, OUTPUT);
Serial1.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1,RXD,TXD);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(FC, HIGH); // Make FLOW CONTROL pin HIGH
Serial1.println("RS485 01 SUCCESS"); // Send RS485 SUCCESS serially
delay(500); // Wait for transmission of data
digitalWrite(FC, LOW); // Receiving mode ON
while (Serial1.available()) { // Check if data is available
char c = Serial1.read(); // Read data from RS485
Serial.write(c); // Print data on serial monitor
}
delay(1000);
}Built-in OLED Display #
| Display driver | SSD1306 |
| Communication | I2C |
| Module Address | 0x3C |
| Resolution | 128 x 64 |
Programming OLED Display #
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels
// Declaration for an SSD1306 display connected to I2C (SDA, SCL pins)
#define OLED_RESET -1 // Reset pin # (or -1 if sharing Arduino reset pin) Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET);
void setup() {
Wire.begin(16,17);
if(!display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C)) {
// Address 0x3C for 128x64 Serial.println(F("SSD1306 allocation failed"));
for(;;); // Don't proceed, loop forever
}
// Show initial display buffer contents on the screen –
// the library initializes this with an Adafruit splash screen.
display.display(); delay(2000); // Pause for 2 seconds
}
void loop() {
}Built-in Buttons #
| Read mode | ADC (Analog to Digital Conversion) |
| Analog IO | GPIO36 |
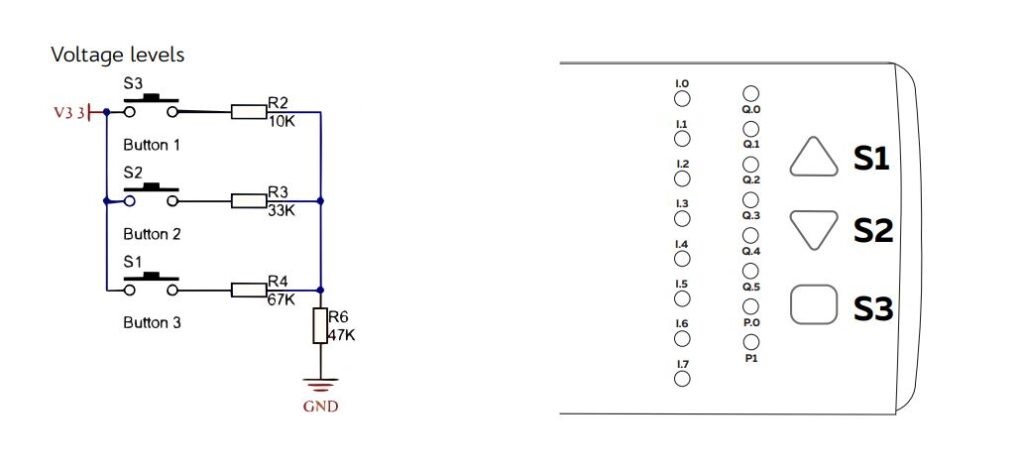
Programming Buttons #
#define buttonPin 36
int buttonState = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(buttonPin,INPUT);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Button: ");
buttonState = analogRead(buttonPin);
delay(50);
Serial.print(analogRead(buttonPin));
Serial.print("\tAnalog: ");
delay(1000);
}GSM Communication #
| Model of GSM Modem | SIM800 |
| FCC ID | UDU-SIM800C |
| TAC | 86610402 |
| RXD | GPIO33 |
| TXD | GPIO32 |
Programming GSM Communication #
#define GSM_RX 33
#define GSM_TX 32
unsigned long int timer1 = 0;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Hello");
Serial2.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, GSM_RX, GSM_TX);
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT+CPIN?");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT+CFUN?");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
Serial.println("AT TIMEOUT");
}
void loop() {
while (Serial.available()) {
int inByte = Serial.read();
Serial2.write(inByte);
}
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
}RESET and USB #