Programming #
The NORVI EC-M11-EG-C3-B95 has a mini USB port for serial connection with the SoC for programming. Any ESP32-supported programming IDE can be used to program the controller. Follow this Guide to programming NORVI ESP32 controllers with the Arduino IDE.
SoC: ESP32-WROOM32
Programming Port: USB UART
8-pin Connector and wire harness #
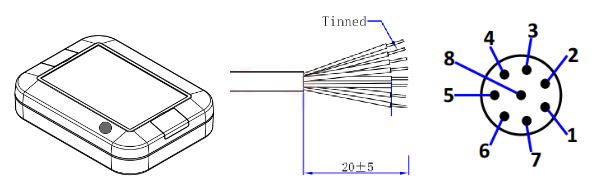
Pin Description #
| 8P Male | Wire color | I/O Configuration |
| 1 | White | A+ |
| 2 | Brown | A- |
| 3 | Green | B+ |
| 4 | Yellow | B- |
| 5 | Gray | RS-485A |
| 6 | Pink | RS-485B |
| 7 | Blue | Power+ |
| 8 | Red | Power- |
Load Cell Inputs #
Programming Load Cell Inputs #
| Number of Load Cell Inputs | 1 |
| Module Type | HX711 |
| PD SCK | GPIO32 |
| DOUT | GPIO33 |
#include "HX711.h"
const int LOADCELL_DOUT_PIN = 33;
const int LOADCELL_SCK_PIN = 32;
HX711 scale;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("HX711 Demo");
Serial.println("Initializing the scale");
scale.begin(LOADCELL_DOUT_PIN, LOADCELL_SCK_PIN);
scale.set_scale(2280.f);
// this value is obtained by calibrating the scale with known weights;
//see the README for details
scale.tare(); // reset the scale to 0
Serial.println("After setting up the scale:");
Serial.print("read: \t\t");
Serial.println(scale.read());
// print a raw reading from the ADC
Serial.print("read average: \t\t");
Serial.println(scale.read_average(20));
// print the average of 20 readings from the ADC
Serial.print("get value: \t\t");
Serial.println(scale.get_value(5));
// print the average of 5 readings from the ADC minus the tare weight,
//set with tare()
Serial.print("get units: \t\t");
Serial.println(scale.get_units(5), 1);
// print the average of 5 readings from the ADC minus tare weight, divided
Serial.println("Readings:");
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("one reading:\t");
Serial.print(scale.get_units(), 1);
Serial.print("\t| average:\t");
Serial.println(scale.get_units(10), 1);
}RS-485 Communication #
| Driver | MAX485 |
| UART RX | GPIO4 |
| UART TX | GPIO2 |
| Flow Control | GPIO13 |
Programming RS-485 #
NORVI EC-M11-EG series RS-485 connection uses a half-duplex mode of MAX485 transmitter with UART
Communication.
#define RS485_FC 13
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Device Starting");
pinMode(RS485_FC, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(RS485_FC, HIGH); // Turns on Transmitter Mode
Serial.println("RS-485 Sending");
delay(500);
}NB-IoT Module #
| Modem | NB-101 |
| RX | GPIO25 |
| TX | GPIO26 |
| POWER | GPIO22 |
| RESET | GPIO17 |
Programming NB-IoT #
const int GSM_RST = 17; // Define the pin for modem reset
const int GSM_PWR_KEY = 22; // Define the pin for modem power key
const int MODEM_RX = 25; // Define the pin for ESP32's RX to modem's TX
const int MODEM_TX = 26; // Define the pin for ESP32's TX to modem's RX
void setup() {
pinMode(GSM_RST, OUTPUT);
pinMode(GSM_PWR_KEY, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(GSM_PWR_KEY, HIGH); // Set modem to flight mode
digitalWrite(GSM_RST, HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(GSM_RST, LOW);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(GSM_RST, HIGH);
delay(1000);
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize the serial monitor
Serial2.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, MODEM_RX, MODEM_TX);
// Initialize communication with modem
Serial.println("SIM AT START >>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
delay(2000);
Serial.flush();
Serial2.println("AT+NCONFIG=AUTOCONNECT,TRUE");
delay(2000);
while (Serial2.available()) {
char response = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(response);
}
Serial2.println("AT");
delay(2000);
while (Serial2.available()) {
char response = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(response);
}
Serial2.println("AT+CEREG?");
delay(2000);
while (Serial2.available()) {
char response = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(response);
}
Serial.flush();
}
void loop() {
Serial.print(".");
Serial2.println("AT");
while (Serial2.available()) {
char response = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(response);
}
delay(5000);
Serial2.println("AT+CEREG?");
delay(2000);
while (Serial2.available()) {
char response = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(response);
}
}



