In the realm of industrial automation, the integration of advanced technologies has become paramount to enhance efficiency, connectivity, and real-time monitoring. One such powerful combination is GSM Integration in Industrial PLCs as using ESP32 and Arduino-powered Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) equipped with GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) connectivity. This article delves into the capabilities of ESP32 and Arduino in the context of PLCs, highlighting the advantages of GSM integration for seamless communication in industrial applications, especially for the NORVI GSM series.
ESP32 and Arduino: A Dynamic Duo

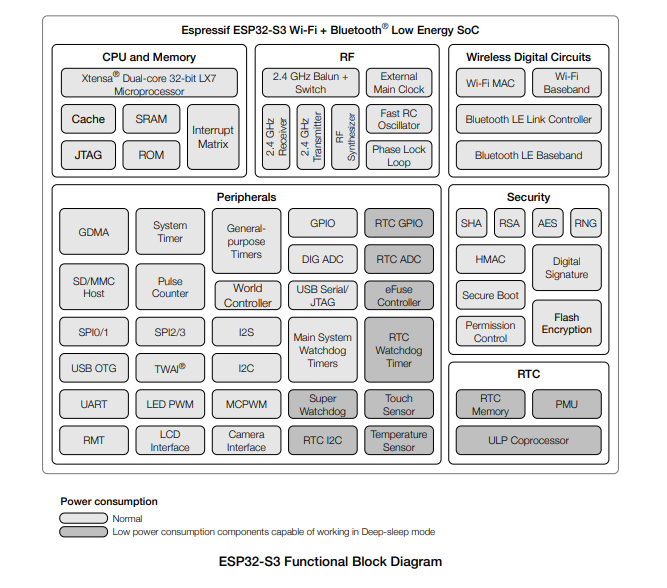
The ESP32, developed by Espressif Systems, and Arduino, an open-source electronics platform, have become popular for building robust and flexible PLCs. The ESP32 offers a dual-core processor, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and a rich set of peripherals, making it ideal for industrial automation applications. Arduino, with its easy-to-use development environment, extensive community support, and a wide array of compatible shields, complements the ESP32 to create a powerful combination for PLCs.
Key Features of ESP32 and Arduino for PLCs
- Dual-Core Processing: The dual-core architecture of ESP32 enables multitasking, allowing simultaneous execution of control algorithms and communication tasks.
- Wireless Connectivity: ESP32’s built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities provide wireless communication options, facilitating easy integration into existing networks.
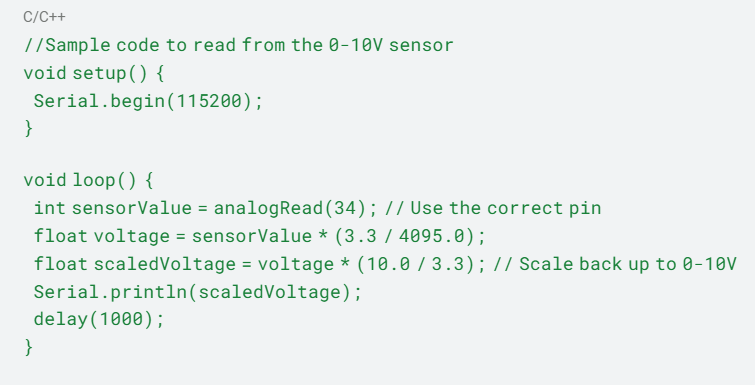
- Rich Peripheral Set: Both ESP32 and Arduino offer a diverse range of GPIO pins, analog inputs, and communication interfaces, allowing for seamless integration with sensors, actuators, and other industrial devices.
- Open-Source Ecosystem: Arduino’s open-source nature fosters a collaborative community, resulting in a vast library of pre-built functions and shields that can be readily employed in PLC projects.
GSM Integration in Industrial PLCs
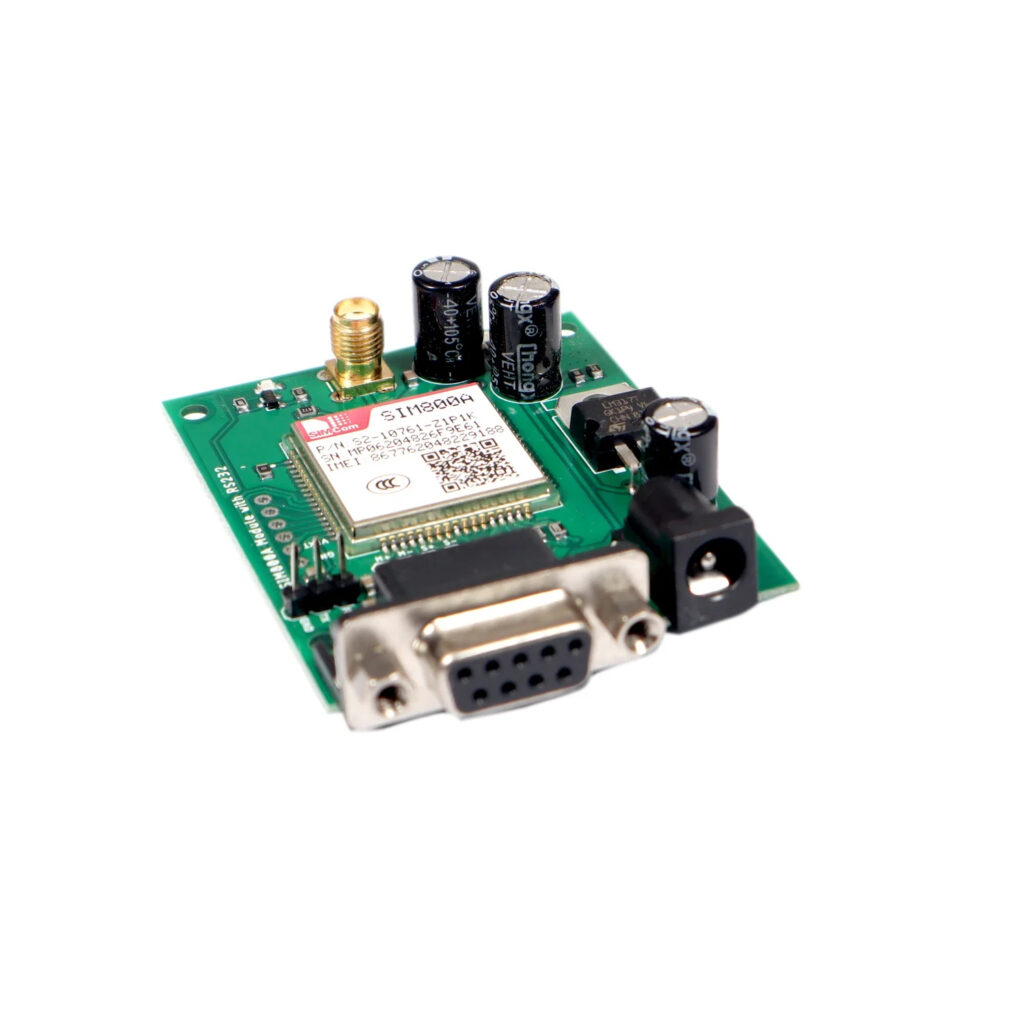

GSM technology plays a pivotal role in enabling remote communication for industrial systems. By integrating GSM modules with ESP32 and Arduino-powered PLCs, several benefits are realized. Refer to the following benefits of GSM Integration in Industrial PLCs.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: GSM connectivity empowers PLCs to transmit real-time data and receive control commands remotely. This capability is crucial for industries where on-site presence is limited or not feasible.
- Data Logging and Analysis: PLCs equipped with GSM can log data and send it to a centralized server for analysis. This facilitates predictive maintenance, process optimization, and data-driven decision-making.
- Alerts and Notifications: Instantaneous communication through GSM enables prompt alerting in case of critical events or system failures. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and enhances overall system reliability.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The modular nature of both ESP32 and Arduino allows for easy scalability. Additional GSM modules can be integrated to accommodate growing communication requirements, making the system highly flexible.
Case Study: Industrial Application of ESP32 and Arduino PLC with GSM
There are many case studies related to GSM Integration in Industrial PLCs. Let’s consider a practical example of an industrial water treatment plant that employs an ESP32 and Arduino-powered PLC with GSM connectivity.
- Sensor Integration: The PLC interfaces with sensors measuring water quality, flow rates, and tank levels, utilizing the GPIO and analog inputs.
- Control Algorithms: The dual-core processing capability of ESP32 allows for the implementation of sophisticated control algorithms to regulate chemical dosing, pump speeds, and valve positions based on real-time sensor data.
- GSM Communication: The PLC is equipped with a GSM module to transmit data on water quality, system status, and operational parameters to a centralized control center.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Plant operators can remotely monitor the water treatment process, receive alerts for critical events, and adjust control parameters through a secure GSM connection.
- Data Logging and Analysis: Historical data is logged and transmitted to a cloud-based server for analysis. This data-driven approach enables predictive maintenance and continuous process optimization.
Conclusion
The integration of ESP32 and Arduino into PLCs and GSM connectivity opens up new possibilities for industrial automation. This dynamic duo provides a cost-effective, scalable, and flexible solution for diverse applications, ranging from manufacturing to water treatment. The ability to remotely monitor, control, and analyze industrial processes in real-time enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and ultimately contributes to a more sustainable and connected industrial ecosystem. As technology continues to advance, the synergy between ESP32, Arduino, and GSM holds immense potential for shaping the future of industrial automation. Therefore, GSM Integration in Industrial PLCs are creates the innovative industrial automation projects even better.

NORVI has ESP32-based and Arduino-powered Devices which has GSM connectivity which comes as the NORVI GSM series. Visit the product page Now: https://norvi.lk/product/esp32-gsm-series/
Or, Contact us at [email protected]