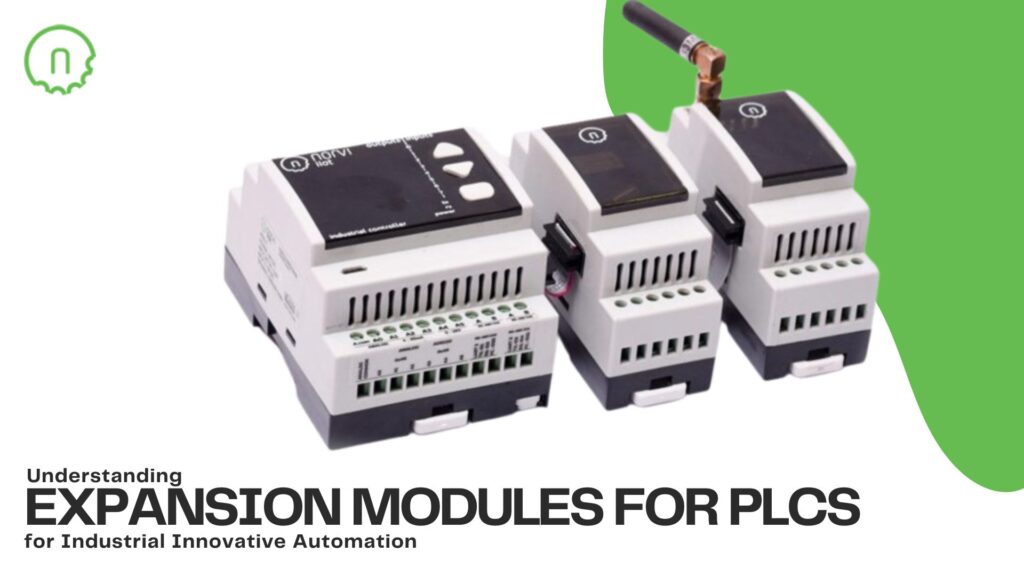
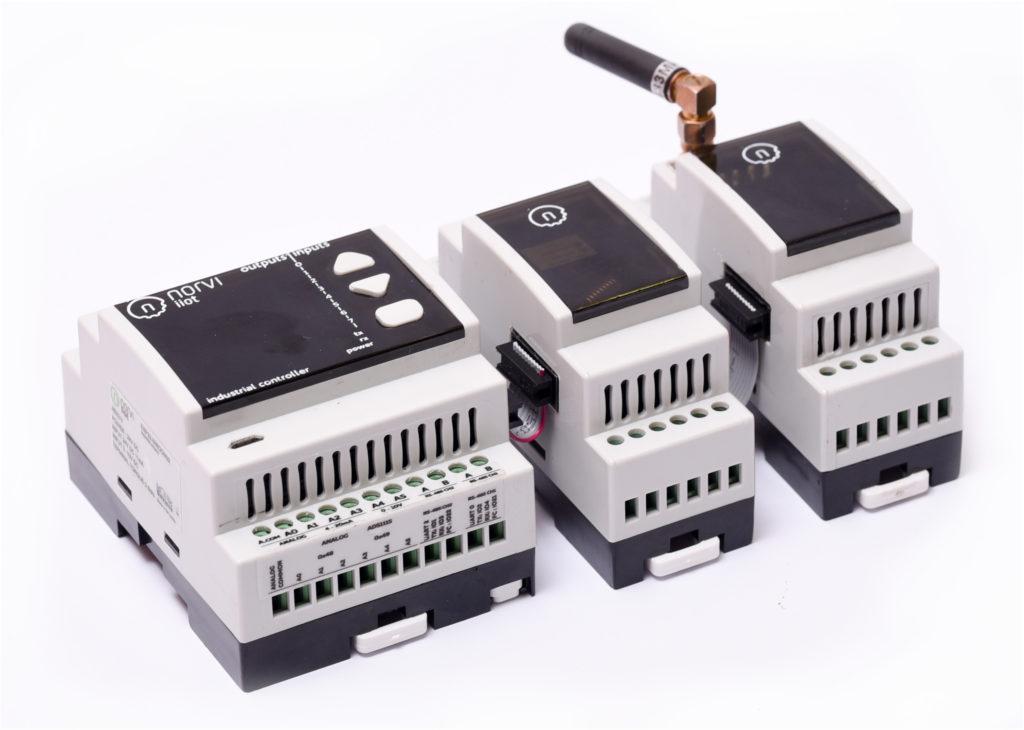
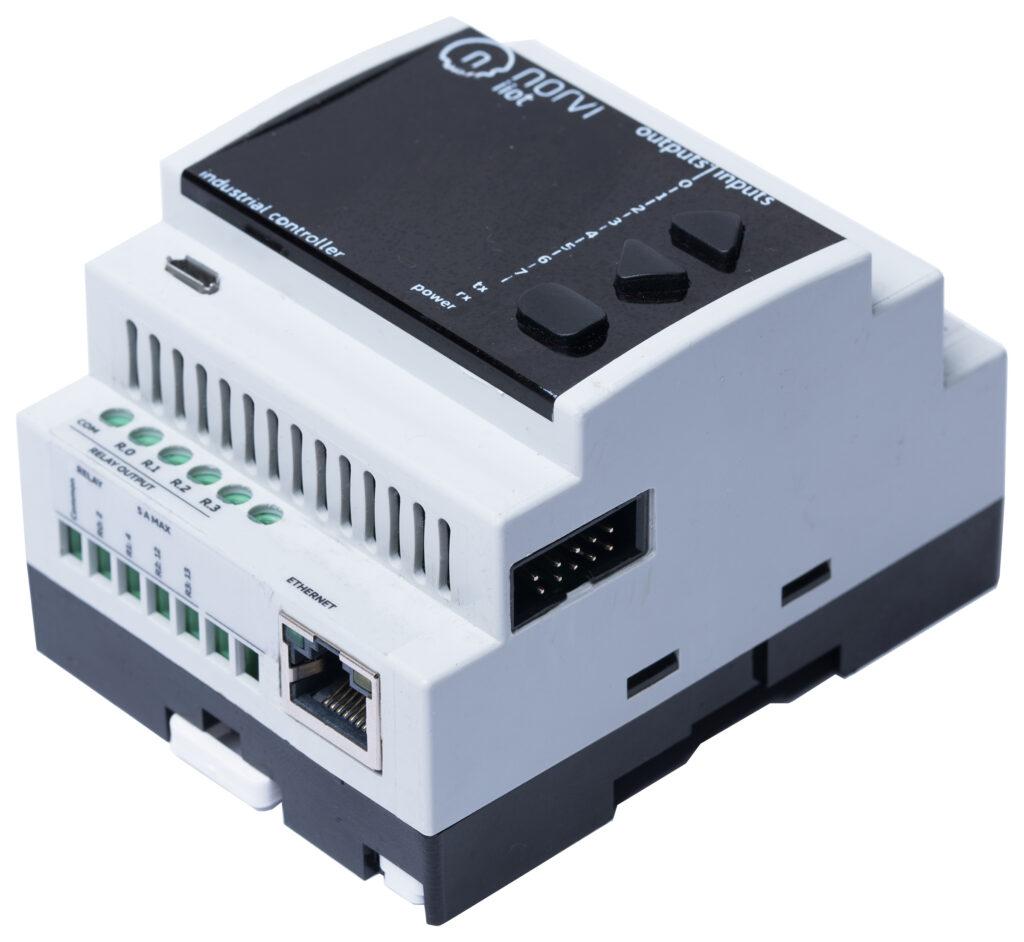
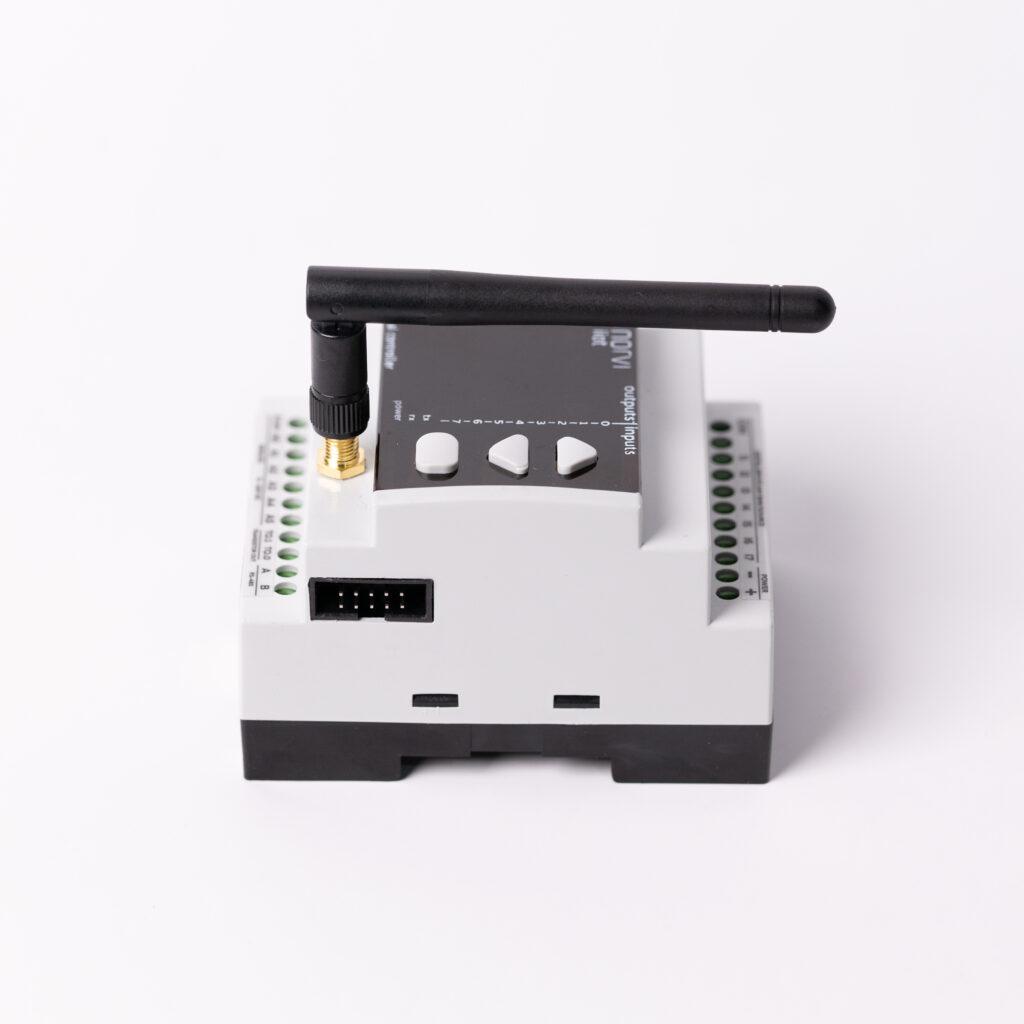
Discover the transformative role of Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control industrial automation. Explore their efficiency, reliability, and adaptability in managing signaling and light load control tasks through this article.
In the world of industrial automation and control systems, the use of transistor outputs has become increasingly prevalent due to their efficiency, reliability, and versatility in handling various tasks, especially in signaling and controlling light loads. Transistor outputs serve as essential components in interfacing between digital control systems and external devices, offering a means to drive and control numerous applications in industrial settings.
What are Transistor Outputs?
Transistor outputs refer to the utilization of transistors as the output stage in electronic circuits. Transistors, being semiconductor devices, can serve as switches or amplifiers in various applications. In the context of outputs, transistors are commonly used to control or drive external devices, such as motors, LEDs, relays, or other electronic components.
The primary purpose of transistor outputs is to manage the flow of current or voltage to these external devices based on the input signals received.
By controlling the flow of current or voltage, transistors enable the activation or deactivation of connected loads, making them fundamental in various electronic systems.
Different types of transistors are used as outputs, including bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). Each type has its characteristics and applications. For instance, BJTs are known for their ability to amplify signals and are often used in audio amplifiers. In contrast, FETs are frequently used in switching applications due to their low power consumption and high input impedance.
Transistor outputs find extensive use in industries, especially in automation and control systems. They are crucial in providing precise control, quick response times, and efficient interfacing between digital control systems and external loads or devices. Their reliability, fast switching speeds, and ability to handle various loads make them an integral part of modern electronic circuits, facilitating tasks ranging from signaling to light load control in industrial settings. Therefore, Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control is discussed further through this article.
Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control
Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control are important in the automation industry. Transistor outputs hold immense significance in industrial signaling and the control of light loads due to their reliability, efficiency, and ability to precisely manage electrical signals. Here’s a breakdown of their importance in these specific applications as Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control:
Industrial Signalling:

- Status Indication: Transistor outputs play a pivotal role in indicating the operational status of machinery or systems in industrial settings. LEDs, buzzers, or display panels driven by transistors provide immediate visual or auditory signals, conveying critical information regarding system conditions, faults, or process stages.
- Fault Alarms: They are employed in generating alarms or alerts for malfunctions or abnormal conditions in equipment. Transistors swiftly trigger indicators to notify operators of issues, enabling rapid response and troubleshooting.
- Process Monitoring: In complex industrial processes, transistors help convey real-time data by driving indicators or displays. These outputs offer a clear representation of ongoing processes, aiding operators in monitoring and making informed decisions.
Light Load Control:

- LED Illumination: Transistor outputs efficiently control LED lighting systems. Whether in manufacturing plants or warehouses, transistors regulate the current flow to LEDs, providing illumination for safety, operational, or signaling purposes.
- Small Motors and Solenoids: For machinery requiring low to moderate power, transistors act as switches to control small motors or solenoids. This enables precise control over these devices, contributing to smoother operation and energy efficiency in industrial processes.
- Relay Control: In industrial automation, transistors are used to control relays that, in turn, manage heavier loads. They serve as the interface between low-power control circuits and high-power devices, enhancing safety and reliability.
Advantages in Signalling and Light Load Control:
Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control is a win with the following advantages.
- Efficiency: Transistors provide efficient control over signaling devices and light loads, ensuring minimal energy wastage and optimized performance.
- Quick Response: The rapid switching capabilities of transistors allow for immediate activation or deactivation of signaling elements or light loads, crucial in time-sensitive industrial operations.
- Reliability: Transistors offer robust and consistent performance, reducing the likelihood of failures or malfunctions in signaling systems or light load control applications.
Implementation Considerations:
When employing Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control and industrial automation applications, several factors need consideration:
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the transistors used can handle the voltage and current requirements of the loads being driven.
- Heat Dissipation: Adequate heat sinking or thermal management is crucial, especially when dealing with higher current loads to prevent overheating and damage to the transistors.
- Protection Circuitry: Implement protective measures like diodes, fuses, or transient voltage suppressors to safeguard the transistors from voltage spikes or overcurrent conditions.
- Switching Frequency: Consider the frequency at which the transistors switch to prevent issues related to switching losses and heat generation.
Conclusion
Transistor outputs represent a cornerstone within industrial domains, functioning as pivotal components that enable intricate control mechanisms and steadfast signal transmission across diverse applications. Their intrinsic adaptability, operational efficiency, and adeptness in establishing seamless connections between digital control systems and peripheral devices position them as irreplaceable assets in the realm of contemporary industrial automation.
The indispensability of transistor outputs is underscored by their multifaceted utility. Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control is especially concerned here.They empower precise regulation of electrical currents or voltages, thereby orchestrating the seamless operation of machinery and the dissemination of critical information. Whether illuminating crucial status updates through LEDs, alerting operators to system anomalies via buzzers, or displaying real-time data on control panels, these outputs serve as conduits for swift, accurate communication in complex industrial environments.
Furthermore, their significance extends to the realm of light load management. Transistor outputs adeptly navigate the nuanced control requirements of light loads, orchestrating the optimal functioning of LEDs, small motors, solenoids, and relays. By assuming the role of efficient switches or amplifiers, transistors not only ensure the precise activation or deactivation of these devices but also contribute significantly to energy conservation and streamlined operational efficiency within industrial processes.
The paramount importance of these outputs is accentuated by their trifecta of advantages. Their operational efficiency minimizes energy wastage, ensuring the judicious use of resources within industrial setups. The rapid response capabilities of transistors facilitate instantaneous adjustments in signaling devices or light load controls, fostering a dynamic and responsive industrial ecosystem. Additionally, their inherent reliability and consistency fortify industrial systems against potential failures, bolstering operational continuity and safety.
The optimal harnessing of the potential offered by transistor-based output circuits necessitates meticulous attention to various facets. Prudent selection, adept implementation, and diligent maintenance protocols stand as imperative pillars ensuring not just optimal performance but also longevity and safety within industrial environments. The meticulous orchestration of these circuits elevates their role from mere components to critical assets that underpin the seamless operation and efficiency of industrial processes. Therefore, Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control is vital
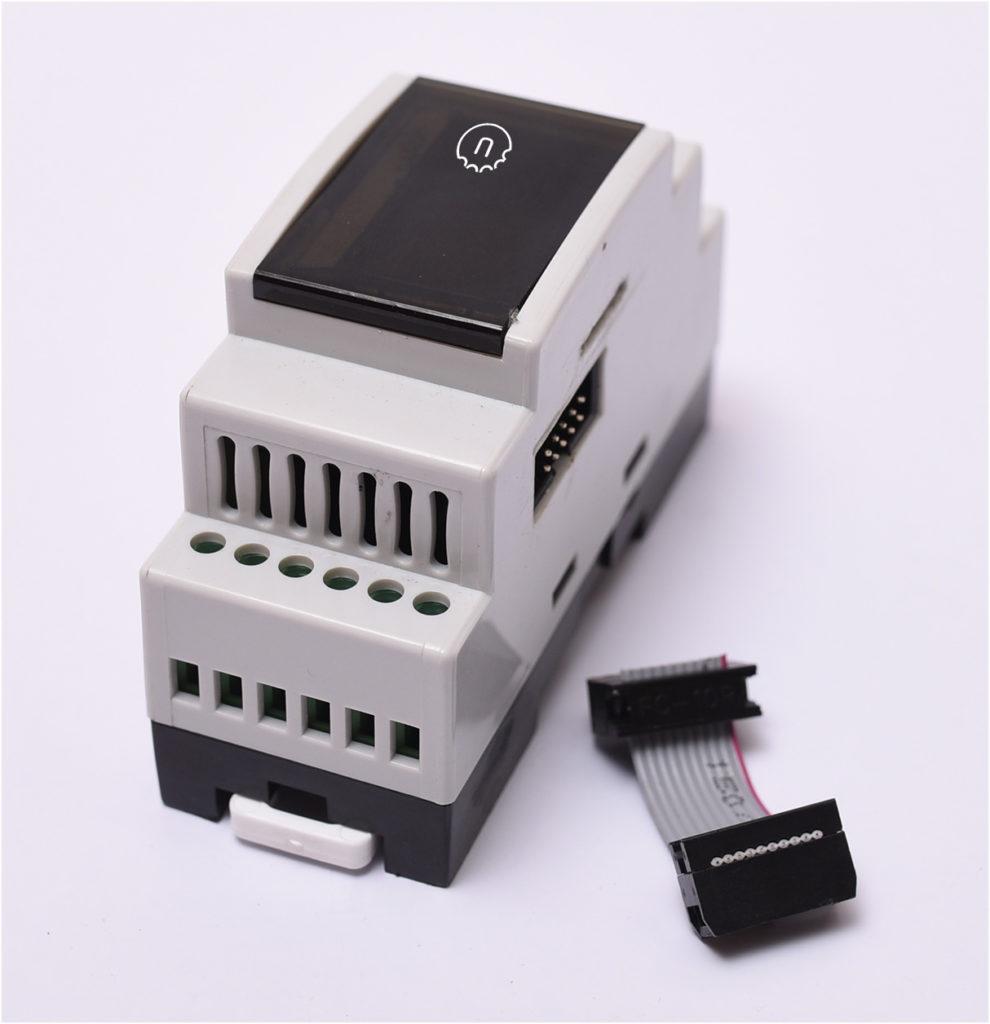

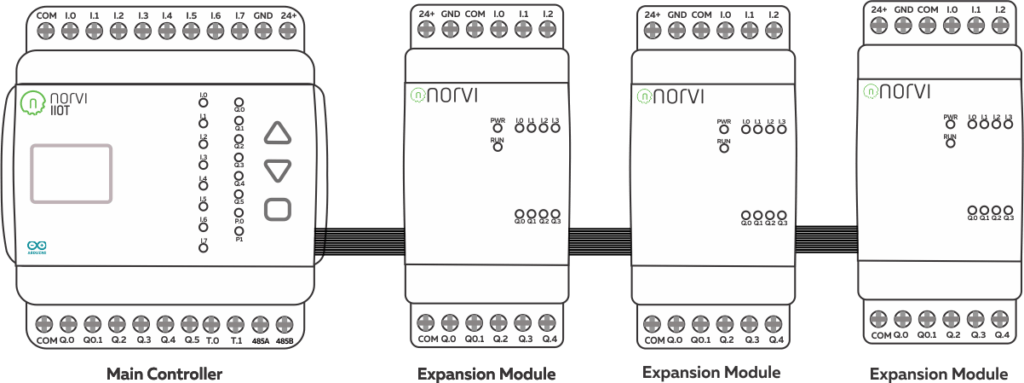
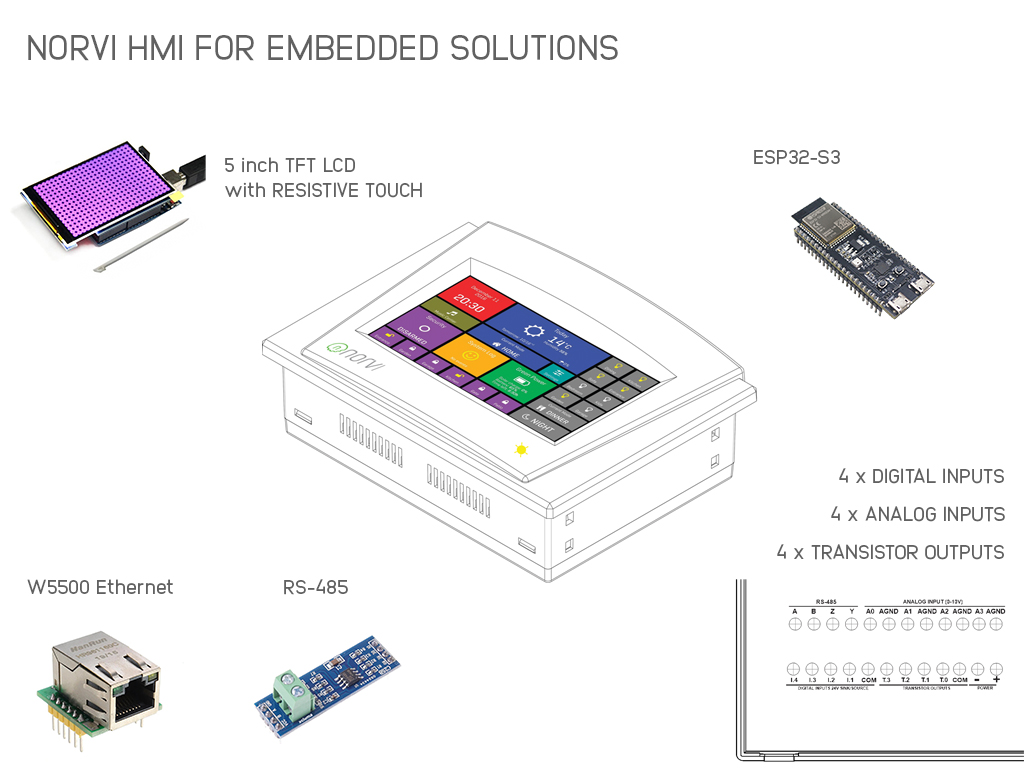
NORVI has Arduino-based ESP32 PLC with Transistor Outputs for Industrial Signaling and Light Loads Control Loads.
BUY NOW or Contact Us at [email protected]