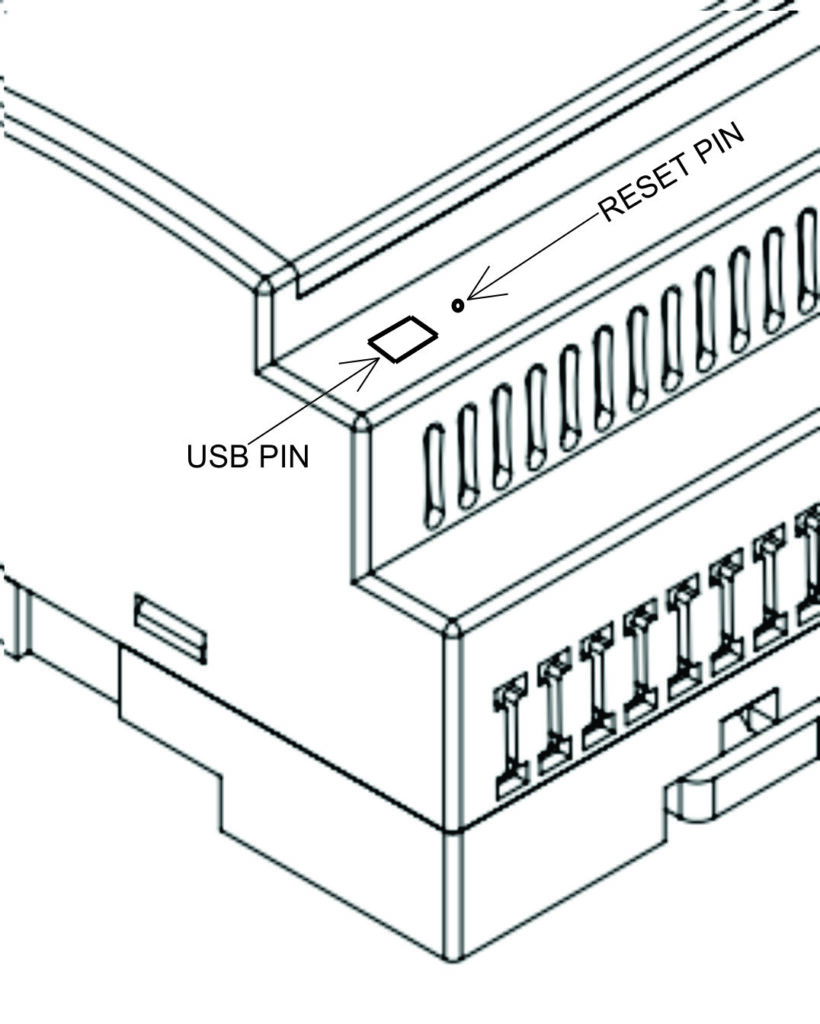
Programming #
The NORVI GSM-AE02-I-G has a mini USB Port for serial connection with the SoC for programming. Any ESP32-supported programming IDE can be used to program the controller. Follow this Guide to programming NORVI ESP32-based controllers with the Arduino IDE.
SoC: ESP32-WROOM32
Programming Port: USB UART
Digital Inputs #
Wiring Digital Inputs #
The digital inputs of NORVI GSM-AE02-I-G can be configured as both Sink and Source connections. The inverse of the Digital Input polarity should be supplied to the common terminal.
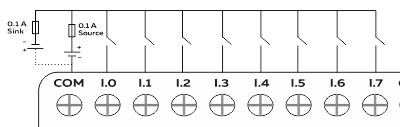
Programming Digital Inputs #
Reading the relevant GPIO of the ESP32 gives the value of the Digital Input. When the inputs are in the OFF state, the GPIO goes HIGH, and when the input is in the ON state, the GPIO goes LOW. Refer to the GPIO allocation table in the datasheet for the digital input GPIO.
#define INPUT1 35
#define INPUT2 34
#define INPUT3 21
#define INPUT4 14
#define INPUT5 13
#define INPUT6 4
#define INPUT7 5
#define INPUT8 15
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Hello");
pinMode(INPUT1, INPUT);
pinMode(INPUT2, INPUT);
pinMode(INPUT3, INPUT);
pinMode(INPUT4, INPUT);
pinMode(INPUT5, INPUT);
pinMode(INPUT6, INPUT);
pinMode(INPUT7, INPUT);
pinMode(INPUT8, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT1));Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT2));Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT3));Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT4));Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT5));Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT6));Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT7));Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT8));
Serial.println("");
delay(100);
}4 – 20 mA Analog Input #
Wiring Analog Inputs #
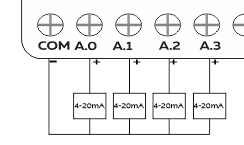
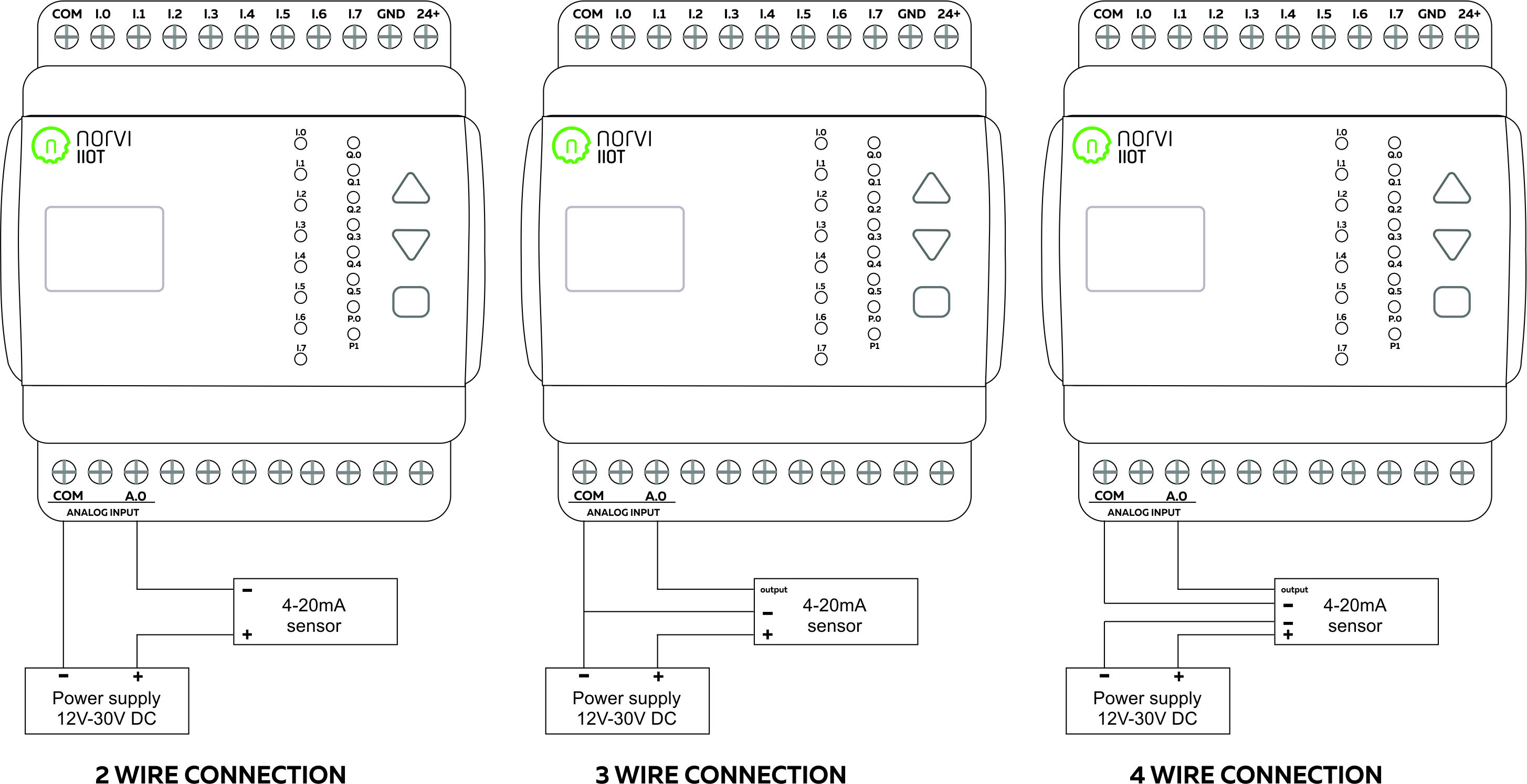
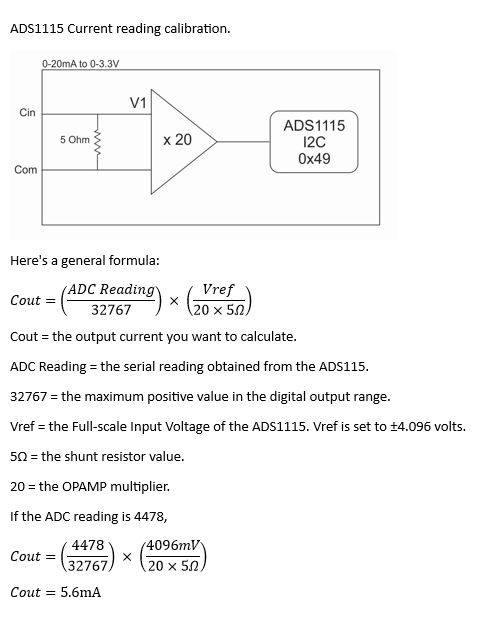
Reading Analog Input #
Reading the relevant I2C address of the ADC gives the value of the Analog Input.
Programming Analog Inputs #
#include <Adafruit_ADS1X15.h>
#include <Wire.h>
Adafruit_ADS1115 ads1;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115000);
Serial.println("Hello");
Wire.begin(16,17);
ads1.begin(0x48);
ads1.setGain(GAIN_ONE);
}
void loop() {
int16_t adc0, adc1, adc2, adc3;
adc0 = ads1.readADC_SingleEnded(0);
adc1 = ads1.readADC_SingleEnded(1);
adc2 = ads1.readADC_SingleEnded(2);
adc3 = ads1.readADC_SingleEnded(3);
float voltage0 = adc0 * 0.155/ 1000*500;
float voltage1 = adc1 * 0.155 / 1000*500;
float voltage2 = adc2 * 0.155/ 1000*500;
float voltage3 = adc3 * 0.155 / 1000*500;
float current0 = voltage0 / shunt_resistance;
float current1 = voltage1 / shunt_resistance;
float current2 = voltage2 / shunt_resistance;
float current3 = voltage3 / shunt_resistance;
Serial.print("Current 0 : "); Serial.print(current0); Serial.println(" mA");
Serial.print("Current 1 : "); Serial.print(current1); Serial.println(" mA");
Serial.print("Current 2 : "); Serial.print(current2); Serial.println(" mA");
Serial.print("Current 3 : "); Serial.print(current3); Serial.println(" mA");
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Push button ");Serial.println(readSwitch());
Serial.println("");
delay(100);
}RS-485 communication #
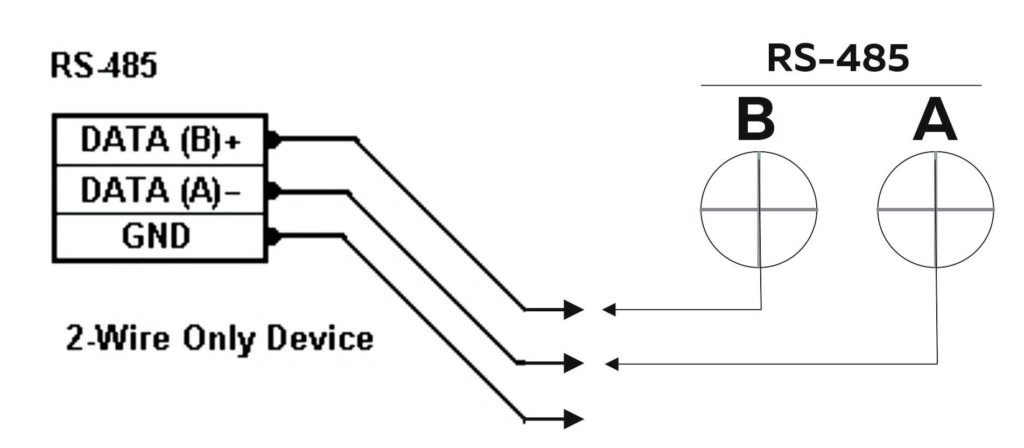
RS-485 Wiring #
| Driver | MAX485 |
| UART RX | GPIO25 |
| UART TX | GPIO19 |
| Flow Control | GPIO22 |
Programming RS-485 #
NORVI-GSM-AE02 series RS-485 connection uses a half-duplex mode of MAX485 transmitter with UART Communication.
#define RS485_RX 25
#define RS485_TX 19
#define RS485_FC 22
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(RS485_FC, OUTPUT);
Serial1.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, RS485_RX, RS485_TX);
digitalWrite(RS485_FC, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(RS485_FC, HIGH);
delay(100);
Serial1.println(F("RS485 01 SUCCESS"));
delay(100);
digitalWrite(RS485_FC, LOW) ;
delay(100);
while (Serial1.available()) {
char c = Serial1.read();
Serial.write(c);
}
delay(100);
Serial.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
}Built-in OLED Display #
| Display driver | SSD1306 |
| Communication | I2C |
| Module Address | 0x3C |
| Resolution | 128 x 64 |
Refer to the GPIO allocation table in the datasheet for the I2C GPIO of the OLED Display.
Library supported by the Adafruit_SSD0306 Library.
Wire. begin (SDA, SCL); is required to initialize I2C on correct pins
Programming OLED Display #
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#include <Adafruit_ADS1X15.h>
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels
#define OLED_RESET -1 // Reset pin # (or -1 if sharing Arduino reset pin)
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET);
void setup() {
Wire.begin(16,17);
if(!display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C)) { // Address 0x3D for 128x64
Serial.println(F("SSD1306 allocation failed"));
for(;;); // Don't proceed, loop forever
}
display.display();
delay(100); //
void loop() {
}Built-in Buttons #
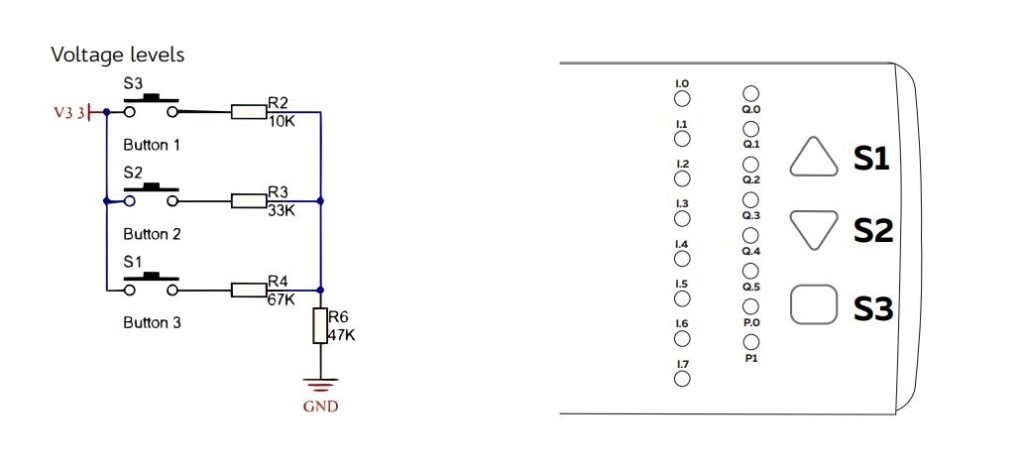
| Read mode | ADC (Analog to Digital Conversion) |
| Analog IO | GPIO36 |
Programming Buttons #
#define ANALOG_PIN_0 36
int analog_value = 0;
int readSwitch(){
analog_value = analogRead(ANALOG_PIN_0);
return analog_value ; //Read analog
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(buttonPin,INPUT);
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("");
Serial.print("Push button ");Serial.println(readSwitch());
Serial.println("");
delay(100);
}GSM Communication #
| Model of GSM Modem | SIM800C |
| FCC ID | UDU-SIM800C |
| TAC | 86610402 |
| RXD | GPIO33 |
| TXD | GPIO32 |
Programming GSM Communication #
#define GSM_RX 33
#define GSM_TX 32
unsigned long int timer1 = 0;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(115000);
Serial.println("Hello");
Serial2.begin(9600, SERIAL_8N1, GSM_TX, GSM_RX);
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT+CPIN?");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT+GSN");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
Serial.println("Testing Modem Done");
}
void loop() {
while (Serial.available()) {
int inByte = Serial.read();
Serial2.write(inByte);
}
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
delay(200);
}RESET and USB #