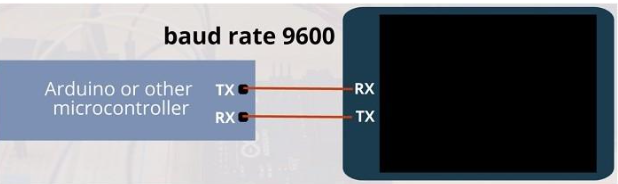
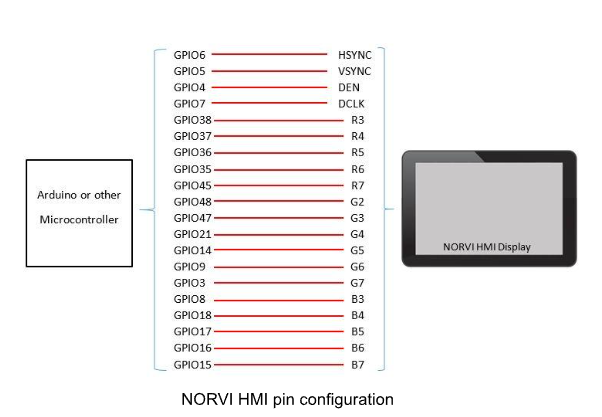
Are you looking to optimize HMI projects for industrial automation success? HMI projects, or Human-Machine Interface projects, are crucial for industrial automation, serving as the vital link between human operators and the technology they use. These projects involve designing, implementing, and optimizing interfaces that allow users to interact with industrial machines, systems, and processes. The seamless integration of HMI solutions is essential for enhancing operational efficiency, ensuring safety, and enabling real-time decision-making in industrial settings.
Importance of HMI Projects in Industrial Automation
HMI projects involve developing interfaces that enable human operators to monitor and control industrial processes and machinery. These interfaces can range from simple touchscreens to complex control panels with advanced functionalities. The significance of HMI projects lies in their ability to streamline operations, improve productivity, and minimize errors by presenting data in a clear and comprehensible manner.
Understanding HMI Software and Hardware
To optimize HMI projects, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the software and hardware components involved.
Software Components and Functionality
HMI software serves as the backbone of the user interface, offering features such as data visualization, alarm management, and historical data access. It enables operators to interact with industrial systems, monitor processes, and respond to critical events in real-time.
Hardware Components and Key Considerations
The hardware components of HMI projects include touchscreens, control panels, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). When selecting hardware, factors such as ruggedness, environmental compatibility, and scalability must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity in industrial environments.
Role of Touchscreens, Control Panels, and PLCs in HMI Projects
Touchscreens provide the tactile interface through which operators interact with the system, while control panels house the necessary controls and indicators for monitoring and managing processes. PLCs serve as the backbone of control and automation, facilitating seamless communication between the HMI interface and the industrial equipment.
| Software Components | Functionality |
| Data visualization | Allows operators to visualize industrial processes |
| Alarm management | Manages and responds to critical events in real-time |
| Historical data access | Provides access to historical data |
| Hardware Components | Key Considerations |
| Touchscreens | Consider ruggedness and environmental compatibility |
| Control panels | Should house necessary controls and indicators |
| PLCs | Facilitate communication between HMI and equipment |
Planning and Designing HMI Projects
The planning and design phase of HMI projects is critical for aligning the interface with user requirements and operational needs.
Gathering and Defining User Requirements
Understanding the specific needs and preferences of end-users is essential for designing an HMI interface that enhances productivity and user satisfaction. This involves gathering input from operators, maintenance personnel, and other stakeholders to define the functional and ergonomic requirements of the interface.
Creating Wireframes and Prototypes
Wireframing and prototyping allow for the visualization and refinement of the HMI interface design before its full-scale implementation. This iterative process enables stakeholders to provide feedback and ensures that the final interface meets the operational objectives.
Selection of Hardware and Software for HMI Projects
Choosing the right hardware and software components is crucial for the successful realization of an HMI project. Factors such as compatibility, reliability, and scalability must be taken into account to ensure that the selected components align with the project’s requirements and long-term goals.
HMI Project Implementation
The implementation phase involves the physical setup, configuration, and integration of the HMI system within the industrial environment.
Installation and Setup
Proper installation and setup of hardware components, including mounting of touchscreens and control panels, are essential to ensure the physical robustness and functionality of the HMI system.
Configuration and Customization
Configuring the HMI software to display relevant data, alarms, and control options in a user-friendly manner is a critical aspect of customization. Tailoring the interface to specific operational needs enhances its usability and effectiveness.
Integration with Existing Systems
Seamless integration with existing industrial control systems, such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and DCS (Distributed Control System), is crucial for ensuring interoperability and data exchange across the entire automation infrastructure.
Best Practices for Reliability, Security, and Scalability
Adhering to best practices in reliability, security, and scalability is paramount during implementation. Redundancy, data encryption, and the use of industry-standard communication protocols contribute to the robustness and resilience of the HMI system.
Programming HMI Interfaces
The programming phase involves the design and implementation of the user interface, control system integration, and advanced feature implementation.
User Interface Design Principles
Adhering to established principles of user interface design, such as clarity, consistency, and feedback, is essential for creating an interface that is intuitive and user-friendly.
Control System Integration and Interactivity
Integrating the HMI interface with the underlying control systems, such as PLCs and industrial controllers, enables real-time data exchange and responsive control of industrial processes.
Implementing Advanced Features and Functionality
Incorporating advanced features, such as trend visualization, predictive maintenance indicators, and remote accessibility, enhances the capabilities of the HMI system and contributes to operational efficiency.
Overcoming Integration Challenges in an HMI Project
When we are working on a implementation of a new HMI project at a manufacturing plant, one of the biggest challenges we faced was integrating the new HMI system with the existing PLCs and control panels. Despite thorough planning and testing, we encountered compatibility issues that threatened to derail the project timeline.
To address this, it should be formed a cross-functional team of software engineers, PLC specialists, and HMI designers. Through collaborative troubleshooting and in-depth analysis, it is able to identify the root cause of the integration issues. By leveraging our collective expertise, it can be reconfigured the communication protocols and made necessary adjustments to ensure seamless integration. This experience is vital as its importance of proactive collaboration and adaptability in overcoming integration challenges in HMI projects.
Testing and Troubleshooting HMI Systems
Thorough testing and troubleshooting are imperative to ensure the reliability and performance of HMI systems in industrial settings.
Importance of Comprehensive Testing and Quality Assurance
Conducting comprehensive testing, including functionality, performance, and usability testing, is crucial to identify and rectify any issues before deployment.
Common Issues, Debugging, and Troubleshooting Strategies
Common issues in HMI systems, such as unresponsive touchscreens or communication errors, require systematic debugging and troubleshooting to identify root causes and implement effective solutions.
Optimization for Performance and Efficiency
Fine-tuning the HMI system for optimal performance involves addressing latency issues, optimizing data retrieval, and streamlining user interactions to maximize operational efficiency.
HMI Project Case Studies
Real-world examples of successful HMI projects provide valuable insights into the practical application and impact of well-executed HMI solutions.
Real-world Examples of Successful HMI Projects
Case studies showcasing HMI projects in diverse industrial domains, such as manufacturing, energy, and transportation, illustrate the tangible benefits and operational improvements achieved through effective interface design and implementation.
Analysis of Challenges Faced and Solutions Implemented
Analyzing the challenges encountered during HMI project implementation and the corresponding solutions applied sheds light on the complexities of industrial automation and the strategies employed to overcome them.
Benefits and Impact on Industrial Automation
Evaluating the tangible benefits, such as increased productivity, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety, highlights the significant impact of well-designed HMI projects on industrial automation.
Future Trends and Innovations in HMI
The landscape of HMI is continually evolving, with emerging technologies and innovative approaches reshaping the future of human-machine interaction in industrial environments.
Exploration of Emerging Technologies in HMI
The exploration of emerging technologies, such as augmented reality interfaces, gesture recognition, and adaptive user interfaces, offers a glimpse into the future of HMI in industrial automation.
Impact and Integration of Augmented Reality Interfaces and Voice Control
The integration of augmented reality interfaces and voice control technologies presents new opportunities for enhancing operator situational awareness and enabling hands-free interaction with industrial systems.
Leveraging Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning in HMI
The integration of predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms into HMI systems holds the potential to enable proactive decision-making, predictive maintenance, and adaptive system behavior based on real-time data analysis.
Best Practices and Tips for HMI Projects
Incorporating best practices and adhering to essential considerations is crucial for the successful execution and long-term success of HMI projects.
Design Principles and Considerations for User Experience
Prioritizing user experience through intuitive design, clear information hierarchy, and ergonomic considerations contributes to the effectiveness and acceptance of HMI interfaces by operators.
Usability, Accessibility, and Human-Centered Design
Ensuring the usability and accessibility of HMI interfaces for diverse user groups, including individuals with varying levels of technical expertise, promotes inclusivity and operational efficiency.
Strategies for Maintenance, Upgrades, and Long-term Success
Implementing proactive maintenance strategies, incorporating upgrade paths for hardware and software, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are essential for ensuring the long-term success of HMI projects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optimizing HMI projects for industrial automation success encompasses a multifaceted approach that spans planning, design, implementation, and ongoing innovation.
The essential components of successful HMI projects include user-centric design, seamless integration, rigorous testing, and adaptability to future technological advancements.
Well-executed HMI projects play a pivotal role in driving efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in industrial automation, empowering organizations to achieve higher levels of productivity and operational excellence. Embracing the latest trends and best practices in HMI is key to staying ahead in the dynamic landscape of industrial automation. By following the outlined strategies and leveraging the latest technologies, organizations can optimize their HMI projects to unlock new levels of efficiency and effectiveness in industrial automation.
NORVI New HMI solution is around the corner, wait with us! till that, connect with us: Facebook : LinkedIn : Twitter
Wanna know more about HMI from NORVI? Read below,
The Rise of HMI Applications: Ultimate Tech Landscape
Thriving HMI Technology: Future of Human-Machine Interface
#HMI #HumanMachineInterface #Technology #IntuitiveUserInterfaces #Industries #hmisolutions #hmiprojects